Remember !
Every wound is a source of infection.
Foreign bodies should not be removed from the wound.
Securing the wound is always beneficial to the
patient .
Wound dressing
If you have a disinfectant, with larger and contaminated wounds it is advisable to use it.
You can also clean the wound with running water .
If there are larger contaminants in the wound, they should be removed.
After removing the dirt and rinsing the wound, possibly disinfecting it, apply a dressing. The best is gauze or dressing gauze made of cotton, and nowadays also made of artificial materials.
If there is more bleeding, additional dressing material in the form of lignin or gauze can be placed on the gauze, which, in addition to pressure, will absorb the blood. The dressing prepared in this way can be fixed with an adhesive, and if the dressing is larger – with a woven bandage (bandage) or elastic bandage.
If there is a lot of bleeding from the wound, apply a pressure dressing to the bleeding site. This involves applying a thicker layer of dressing – first gauze and then another layer of gauze or lignin and bandaging over a slightly larger area.
In situations of rapid hemorrhage, do not pull any foreign bodies out of the wound, but dress it with a sterile dressing . The dressing must adhere well to the wound, so it is better to fix it with a woven cotton or elastic bandage. If the dressing is soaked with blood, do not remove it, but put another dressing on top and bandage it.
You can also use a triangular sling in an emergency situation. You can use the sling to attach, for example, an upper limb to your chest. Immobilizing the injured limb in this way reduces bleeding and the risk of additional injuries.

Remember!
Wear disposable gloves.
Be careful that blood does not get into your eye, nose or
mouth.
Taming the bleeding
Instruct the injured person to sit on the ground .
While you are looking for a bandage or gloves, instruct him to apply firm pressure with his hand to the bleeding area.
The dressing can be sterile gauze or a rolled up bandage.
Apply direct pressure to the bleeding site with the dressing or your hand .
If you can, fix the dressing with a bandage, without reducing the pressure on the wound (if you can’t or don’t have a bandage – stay with hand pressure) .
If blood is still flowing, improve the pressure and add more layers of dressing .
Do not release the compression.
If the person who is hemorrhaging :
Will turn pale
Will feel sudden weakness
Will start to fall asleep or lose consciousness
Will break into a sweat
While waiting for the arrival of the emergency medical team:
Lay the victim on his back and if you do not suspect a spinal injury,
with legs elevated.
Inform the medical dispatcher (112) that the victim’s condition has deteriorated.
Talk to him to control his consciousness.
Control the bleeding site, do not reduce pressure.
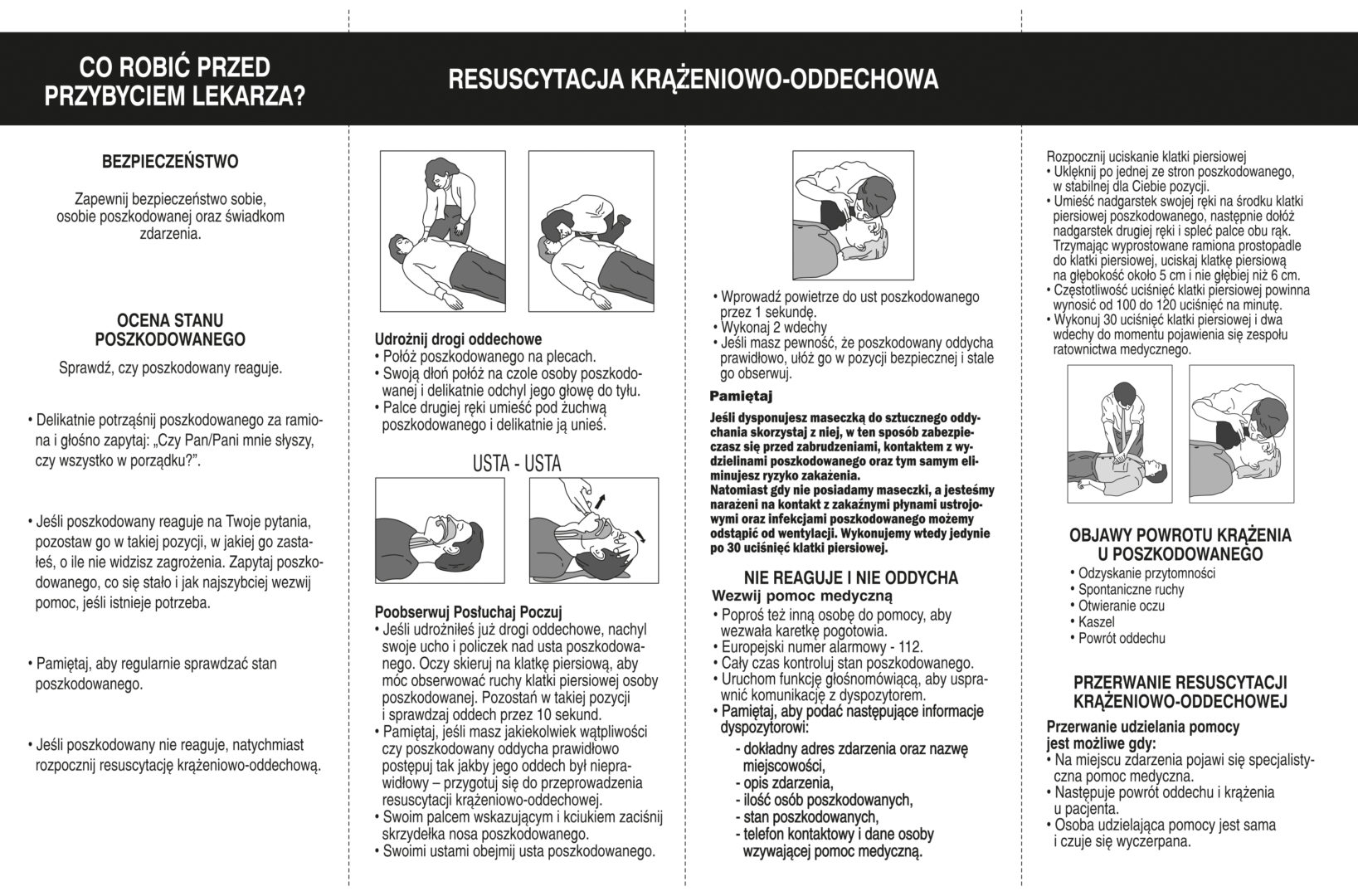
If he loses consciousness, start cardiopulmonary resuscitation .
Proceedings
Make sure the place is safe.
Assess the condition of the injured person; if necessary, call for medical help .
Do not straighten or move parts of the body suspected to be broken by the injury.
Dress visible wounds.
Apply a cold compress (such as a cloth-wrapped bag of water and ice) to the injury site.
Elevate the injured body part, if it does not cause severe pain.
You can immobilize the limb by following the following rules: in the case of a bone fracture, immobilize two adjacent joints (for example, in the case of a forearm fracture, immobilize the elbow joint and the wrist). For immobilization, you can use any object of appropriate length, adapted to the shape of the limb (not vice versa) and that does not injure the skin.
Immobilize the injured person at the scene and notify the ambulance service if you suspect a fracture of a bone in the lower limb, pelvis, spine or skull.
An effective way of not immobilizing the upper limb is to put on a triangular sling creating a so-called Temblak . If you do not have a sling you can make one yourself and, for example, from a T-shirt .
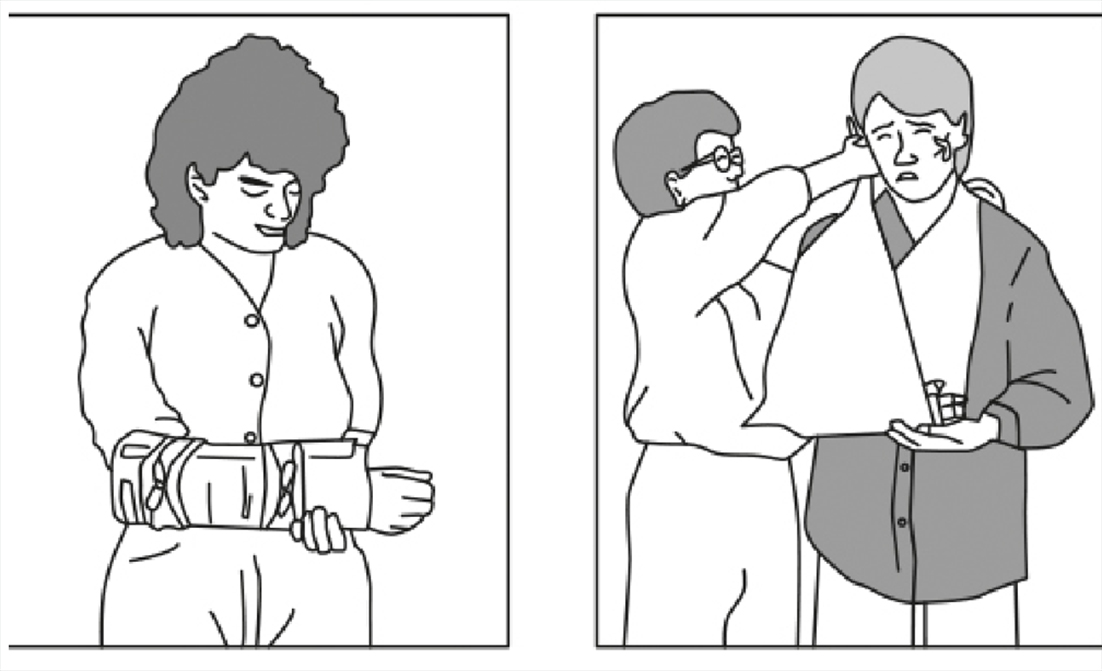
Consider calling for medical help if: the limb below the site of injury turns blue, is cool to the touch (blood vessel damage), becomes numb, there is sensory disturbance (nerve injury), or the slightest movement causes the victim severe pain.